Navigating the complexities of university grading systems can be a daunting task for prospective students, current undergraduates, and even graduate students. Understanding how your academic performance is evaluated is crucial for academic success, scholarship applications, graduate school admissions, and even future employment prospects. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the various grading systems employed by universities, providing a clear and concise explanation of GPA calculations, letter grades, and other important aspects of academic evaluation.
Whether you’re a prospective student researching different universities or a current student aiming to improve your GPA, this guide will provide valuable insights into university grading systems. We’ll explore common grading scales, including the 4.0 scale, the percentage system, and variations thereof. We’ll also delve into the significance of grade point averages, how they are calculated, and their impact on your academic standing. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a strong understanding of how university grading systems work and how to interpret your academic performance effectively.
How GPA Is Calculated
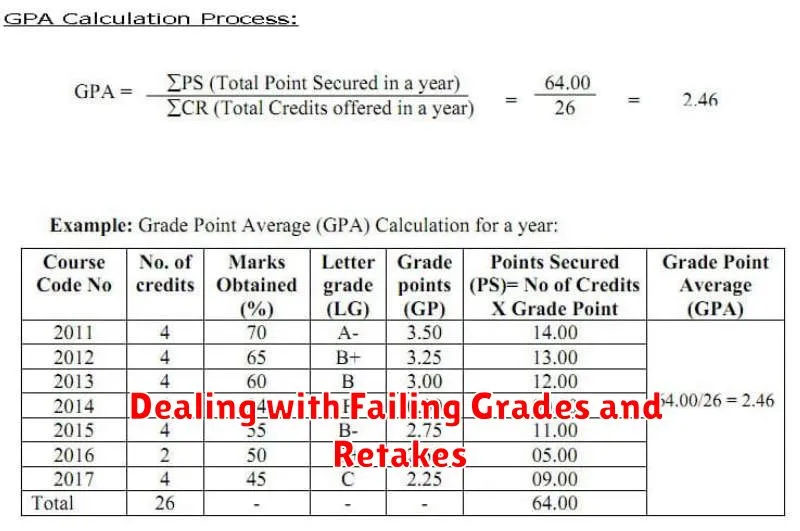
Your Grade Point Average (GPA) is a weighted average that reflects your academic performance. Each grade you receive corresponds to a certain number of quality points.
Typically, an A is worth 4 points, a B is worth 3, a C is worth 2, a D is worth 1, and an F is worth 0. This scale may vary slightly between institutions. Your GPA is calculated by multiplying the quality points for each course by the number of credit hours for that course, summing these products, and then dividing by the total number of credit hours attempted.
Credit Hours and Course Weight
Credit hours represent the weight of a course in relation to your overall academic workload. They reflect the expected time commitment per week, including class time, study, and assignments.
Courses with more credit hours carry more weight in your Grade Point Average (GPA) calculation. A higher grade in a course with more credit hours will have a greater impact on your GPA than a higher grade in a course with fewer credit hours.
Understanding Pass/Fail and Withdrawals
Pass/Fail grading options offer a non-traditional approach to assessment. A passing grade signifies satisfactory completion, while a failing grade indicates unsatisfactory performance. These options often don’t factor into GPA calculations.
Withdrawing from a course involves officially dropping it after the add/drop period. Deadlines and implications for withdrawals vary. While a “W” may appear on transcripts, it typically doesn’t impact GPA. However, multiple withdrawals could have negative consequences.
It’s crucial to understand your university’s specific policies regarding Pass/Fail and withdrawal options before making a decision. Consult your academic advisor for personalized guidance.
Dealing with Failing Grades and Retakes
Failing a course can be discouraging, but universities often provide avenues for remediation. Understanding your institution’s policies on failing grades is crucial.
Some universities allow retakes, enabling students to improve their grade. This might involve retaking the entire course or just the final exam. Check your university’s specific regulations regarding retake limitations and GPA calculations.
Academic advising is a valuable resource. Advisors can help you understand the implications of a failing grade, explore retake options, and develop strategies for future academic success. Don’t hesitate to reach out for support.
Grade Appeals and Academic Support
If you believe a grade was assigned incorrectly, understand the grade appeal process. Familiarize yourself with deadlines and required documentation. Typically, this involves submitting a written appeal to the professor outlining the basis for your concern.
Universities offer various academic support resources to help students succeed. These may include tutoring services, writing centers, and academic advising. Proactively seeking help can significantly improve academic performance.
How Grades Affect Scholarships and Internships
Your academic performance, reflected in your grades, plays a critical role in securing scholarships and internships. Strong grades demonstrate your commitment to learning and your ability to succeed academically.
Most scholarship committees prioritize candidates with high GPAs. A high GPA increases your competitiveness and chances of receiving financial aid. Similarly, employers offering internships seek students with proven academic excellence, as grades often serve as an indicator of potential workplace performance.
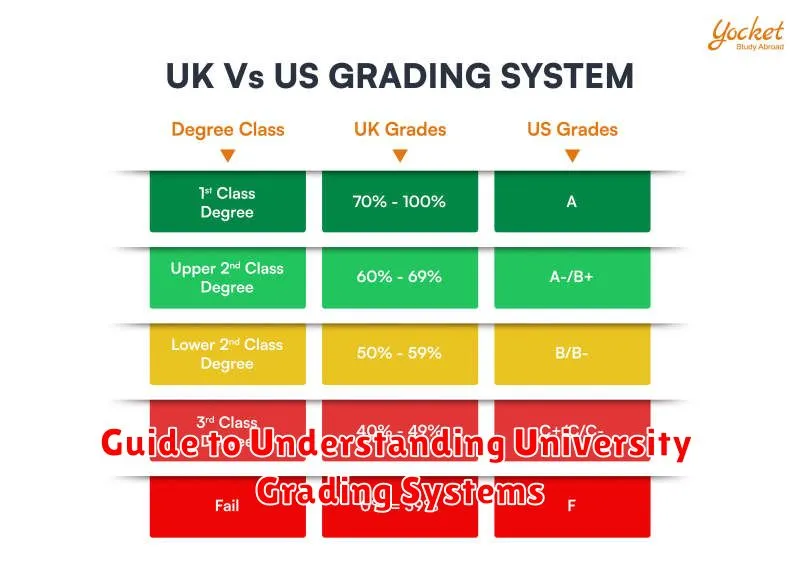
Differences Between Countries
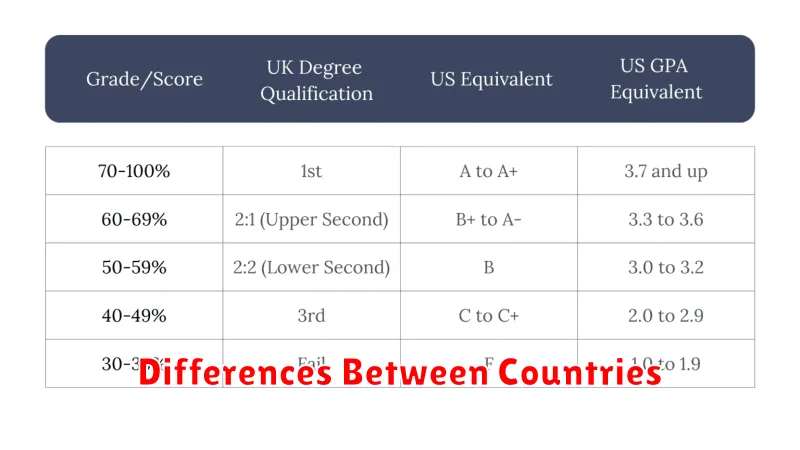
Grading systems vary significantly between countries. Understanding these differences is crucial for students applying to international universities. A grade considered excellent in one country might be average in another.
Some countries use letter grades (A, B, C, etc.), while others use numerical scales (1-10, 1-100, etc.) or percentages. The interpretation of these grades can also differ based on cultural and educational norms.